The Rise of Usage-Based Billing in B2B SaaS
In the ever-evolving landscape of B2B SaaS, pricing models have undergone significant transformations. From the traditional on-premise software sold with perpetual licenses to the per seat pricing in the cloud era, the journey of software monetization has been marked by adaptation to changing business needs and technological advancements.
However, one of the most notable shifts in recent years has been towards usage-based billing—a model that aligns pricing directly with value delivered, revolutionizing the way businesses pay for software services.
Origins of Usage-Based Billing
The origins of usage-based billing can be traced back to the emergence of cloud computing. As software migrated from on-premise installations to the cloud, the subscription-based model gained traction, allowing businesses to access software services remotely without the hassle of installation and maintenance. Per seat pricing became a common approach, where companies paid a fixed fee per user, irrespective of actual usage.
However, as SaaS offerings diversified and became more integrated, embedded, or API-based, traditional pricing models began to show limitations. Enter usage-based billing—a dynamic pricing model where customers pay based on their actual usage of the software. This evolution was fueled by the need for fairness and flexibility in pricing, especially in uncertain economic times, where businesses prioritize cost optimization and value maximization.
The Shift towards Usage-Based Pricing
Today, usage-based pricing is increasingly becoming the norm in the B2B SaaS landscape, with three out of five companies incorporating it into their offerings. This shift is driven by several factors, including:
Value-Based Pricing: Usage-based billing ensures that businesses pay only for the value they receive, making it a fair and transparent pricing model.
Economic Efficiency: In an era of tight budgets, businesses are keen on optimizing costs. Usage-based pricing allows them to align expenses directly with usage, eliminating wastage on unused seats or features.
Improved Metrics: Companies adopting usage-based pricing often experience higher net retention metrics and growth rates, as customers are more likely to scale their usage in line with their needs, leading to increased revenue over time.
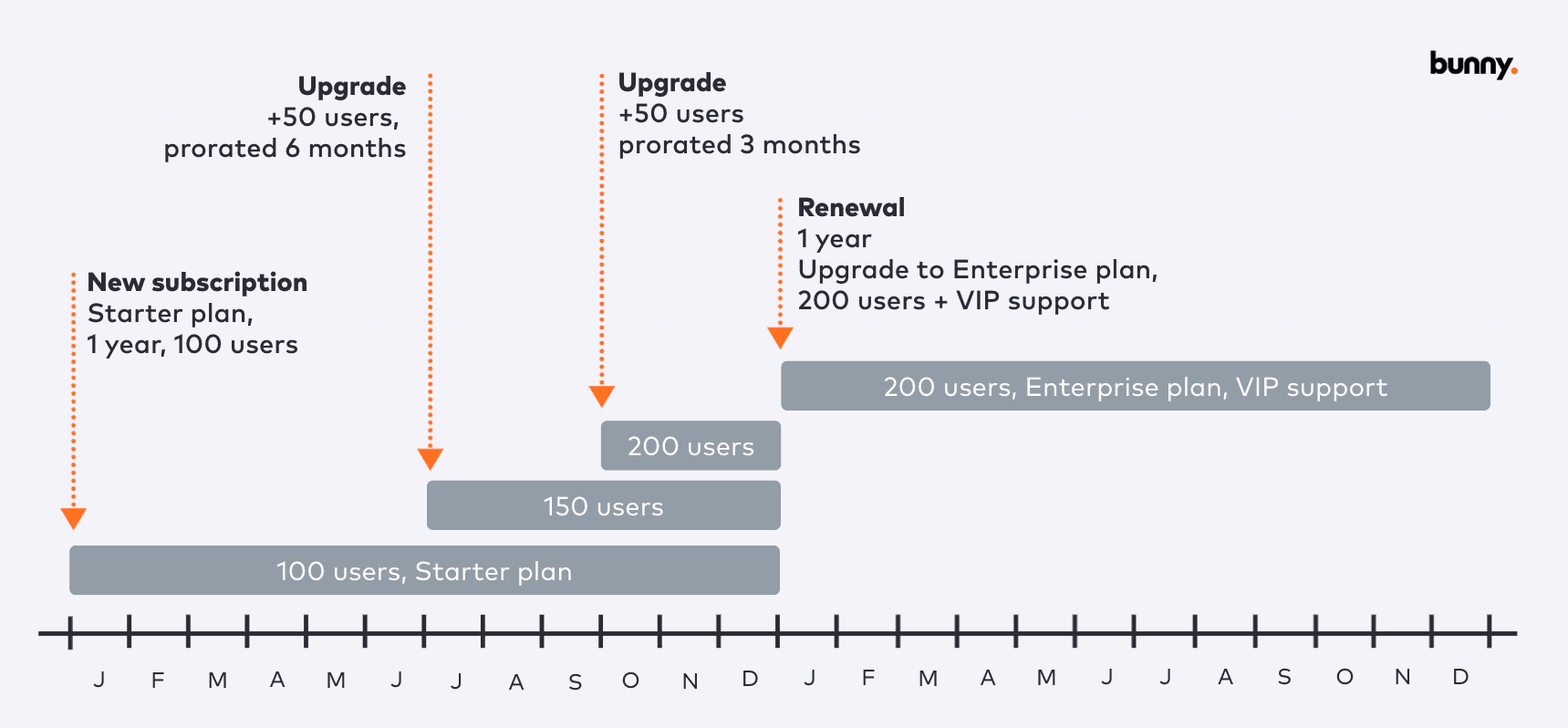
While usage-based pricing is gaining momentum, many companies opt for a hybrid approach, combining seat-based pricing with usage-based billing. This hybrid model caters to diverse customer preferences and allows established SaaS companies to leverage their existing pricing structures while introducing new, consumption-based products.
Choosing the Right Consumption Metrics
The foundation of usage-based pricing lies in selecting the appropriate consumption metrics that not only reflect customer usage but also align with the value they derive from your product. It's crucial to identify features or functionalities that directly contribute to customer success and can be quantified reliably. For instance, an e-signature company might track the number of documents signed as a consumption metric. As customers sign more documents, they inherently receive greater value from the service, making it a logical metric for pricing.
When selecting consumption metrics, consider the following factors:
Value Alignment: Ensure that the chosen metrics accurately reflect the value proposition of your SaaS offering. Customers should perceive an increase in usage as an indication of enhanced value received.
Measurability: Opt for metrics that can be tracked accurately and consistently over time. Leverage analytics tools and data insights to monitor usage patterns and identify trends.
Scalability: Choose metrics that can scale with your customers' growth and evolving needs. Scalable metrics ensure that pricing remains equitable and sustainable as customer usage expands.
Technical Requirements for Implementation
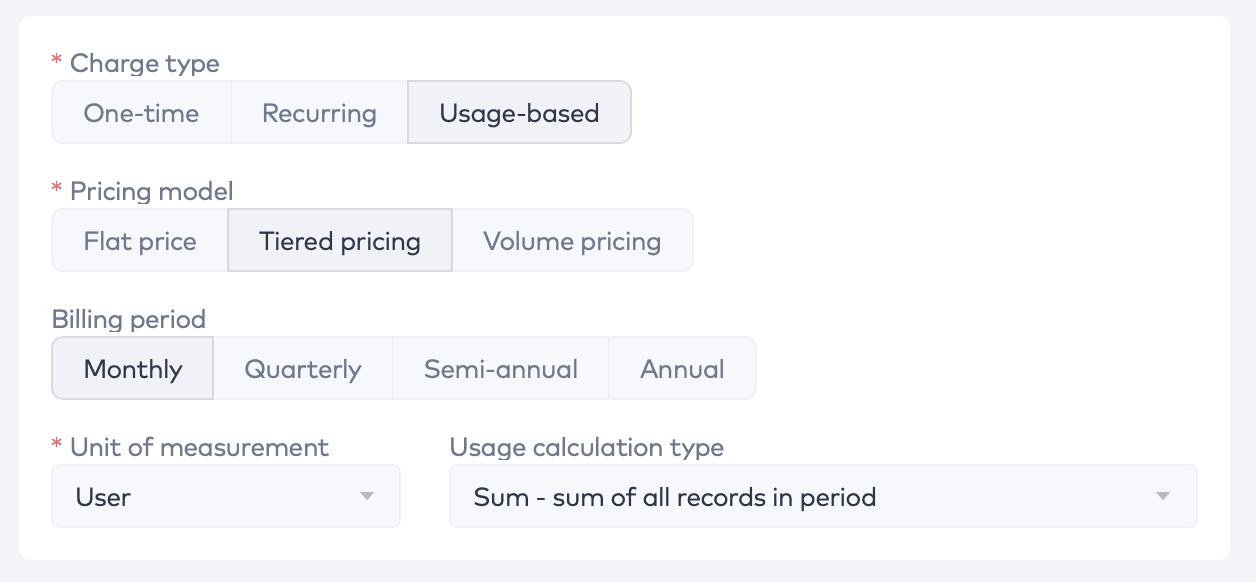
Implementing usage-based pricing requires robust technical infrastructure to monitor usage metrics effectively and generate accurate invoices. This process typically involves two key components: usage metering or collection and invoice generation.
Usage Metering or Collection
Data Collection: Implement mechanisms to collect and aggregate usage data from your SaaS platform in real-time. Leverage APIs, event tracking, or custom instrumentation to capture relevant usage metrics.
Metric Processing: Process the collected usage data to calculate consumption metrics accurately. Employ data pipelines or stream processing frameworks to handle large volumes of data efficiently.
Monitoring and Alerts: Set up monitoring and alerting systems to detect anomalies or irregularities in usage patterns. Proactively address issues to ensure accurate billing and customer satisfaction.
Invoicing
Tiered Pricing Structures: Define tiered pricing models based on usage thresholds or tiers. Establish pricing tiers that align with customer segments and value propositions.
Pricing Calculation: Develop algorithms or scripts to calculate pricing based on usage metrics and tiered pricing structures. Apply appropriate pricing logic to determine the amount to be invoiced for each customer.
Invoice Generation: Generate invoices automatically based on usage data and pricing calculations. Integrate with billing systems or invoicing platforms to streamline the invoicing process and ensure accuracy.
In conclusion, implementing usage-based pricing in your SaaS offering is a transformative endeavor that requires a strategic blend of customer-centricity and technical prowess. By carefully selecting consumption metrics that align with customer value and investing in robust technical infrastructure, you can create a pricing model that not only fosters transparency and fairness but also drives sustainable growth and customer satisfaction.
By choosing metrics that directly correlate with the value proposition of your SaaS solution, you ensure that increased usage translates to enhanced customer value. Whether it's tracking the number of documents signed in an e-signature platform or monitoring API calls in an integration service, the key is to select metrics that accurately reflect the utility and impact of your product on the customer's business.
On the technical front, establishing reliable mechanisms for usage metering, data processing, and invoice generation is paramount. Leveraging modern technologies such as APIs, event tracking, and data processing frameworks enables you to collect and process usage data efficiently, while tiered pricing structures and automated invoicing systems streamline the billing process and ensure accuracy.
In essence, the successful implementation of usage-based pricing empowers your SaaS business to deliver value-driven pricing, improve customer retention, and unlock new revenue opportunities. By embracing the symbiotic relationship between customer value and technical execution, you can navigate the path to success in the ever-evolving landscape of SaaS pricing models.